Dimensions of vascular cells and of whole veins. The word xylem is derived from the Ancient Greek word ξύλον xylon meaning wood.

Module 3 1 Transport In Plants Xylem And Phloem Diagram Quizlet
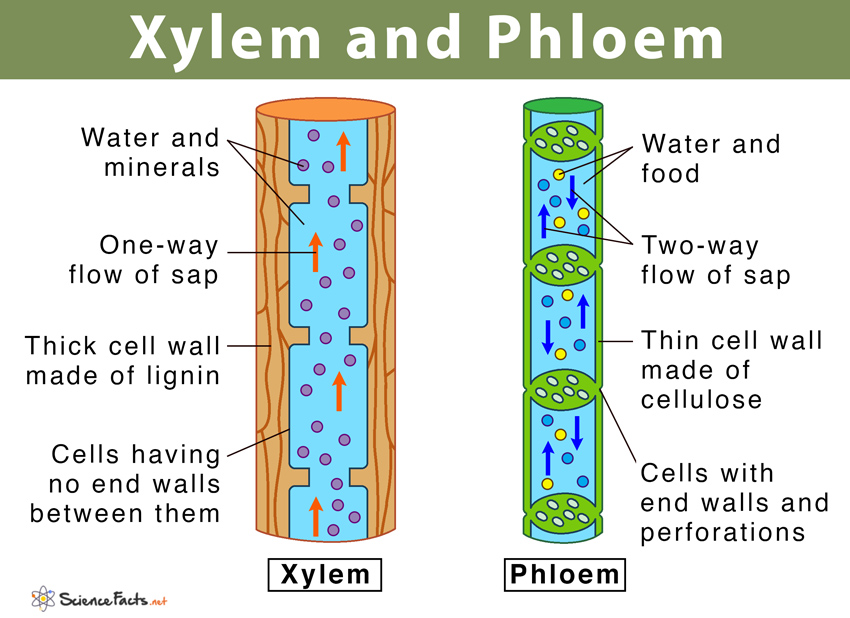
Xylem And Phloem Main Differences Similarities Diagram

Xylem Phloem Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock
Plants perform a similar function of transporting these nutrients what we know as sap by using complex tissues called xylem and phloem.
Function of xylem and phloem. The ground tissue located interior to the cambium ring is referred to as the pith. Together with phloem tissue that conducts sugars from the leaves to the rest of the plant xylem is found in all vascular plants including the. The phloem is made up of living tissue which uses turgor pressure and energy in the form of ATP to actively transport sugars to the plant organs such as the fruits flowers buds and roots.
Phloem ˈ f l oʊ. Photosynthesis is the major function performed by plant cells. Phloem also called bast tissues in plants that conduct foods made in the leaves to all other parts of the plantPhloem is composed of various specialized cells called sieve tubes companion cells phloem fibres and phloem parenchyma cells.
əm FLOH-əm is the living tissue in vascular plants that transports the soluble organic compounds made during photosynthesis and known as photosynthates in particular the sugar sucrose to parts of the plant where needed. This transport process is called translocation. In a mature flowering plant or tree most of the cells that make up the xylem are specialised cells called vessels.
The diverse elements of phloem include phloem fibres sieve tubes phloem parenchyma and companion cells. It stores fats starch and tannin etc. Their walls possess pits.
Sieve tubes companion cells phloem fibres and the phloem parenchyma. Transports water and minerals from the roots up the plant stem and into the leaves. Structure of Vascular Tissue.
Xylem fibres are supportive in function. Within the vascular bundles the xylem is located interior to the cambium ring and the phloem is located exterior to the cambium ring accompanied by sclerenchyma ground tissue. The best-known xylem tissue is wood though it is found throughout a plant.
The function of the phloem tissue is to transport food nutrients such as sucrose and amino acids from the leaves and to all other cells of the plant this is called translocation. Extra phloem tissue that carries lots of food allows some pumpkins to grow to enormous sizes. The other material that makes up the vascular plant transport system the xylem.
Phloem is made up of four types of elements. Xylem fibres and Tracheids are made up of lignin which provides structural support to the plant. Check some Scientific Names and Binomial Nomenclature here.
Phloem transports food from leaves to other Parts. Its cell wall is made up of cellulose. The phloem requires inputs of water from the xylem and specialized proteins to help quickly pass the sugars through the plant.
This tissue helps in the transportation of food all through the plant. In trees the phloem is the innermost layer of the bark hence the name derived from the Ancient. Sieve tubes are tubular cells with perforated walls.
Fibres are mainly supportive in function. Sieve tubes companion cells phloem fibres and the phloem parenchyma. Xylem tissue consists of a variety of specialized water-conducting cells known as tracheary elements.
Difference Between Xylem And Phloem. Xylem cells tend to conduct water and minerals from roots to leaves. They transport food prepared by the leaves to different parts of the plants.
In animals this function is performed by the circulatory system. In b monocot stems vascular bundles composed of xylem and. Phloem Cells Phloem cells are other transport cells in vascular plants.
Quaking Aspen leaves are somewhat heart shaped with finely saw-toothed margins and range in size from 125-3 3-8 cm long. Diameters and conductivities of first- second- third- and higher-order minor veins. To understand how these processes work we must first understand the energetics of water potential.
Unlike the xylem phloem conducts in. The phloem and xylem are the main tissues responsible for this movement. Through this channel of phloem cells sugar is transported throughout the plant.
Potential function for xylem and phloem transport gas exchange leaf support and biomechanical strength. You can see this system at work in the veins on plant leaves. Aspens can be identified by their smooth white bark marked by black scars where lower branches are naturally self-pruned.
Primary phloem is formed by the apical meristems zones of new cell production of root and shoot tips. In the center of the stem is ground tissue. In xylem vessels water travels by bulk flow rather than cell diffusionIn phloem concentration of organic substance inside a phloem cell eg leaf creates a diffusion gradient by which water flows into cells and phloem sap moves from source of organic substance to sugar sinks by turgor pressure.
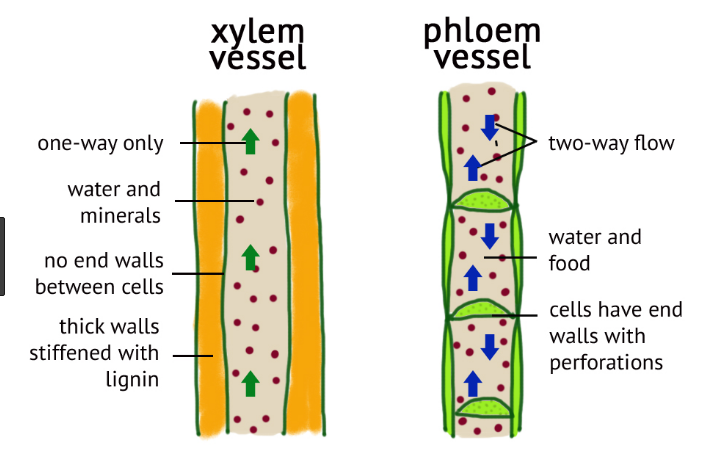
Sclerenchyma fibers cap the vascular bundles. Xylem plant vascular tissue that conveys water and dissolved minerals from the roots to the rest of the plant and also provides physical support. Plants contain vessels which function to transport water and sugars from one part of the plant to anotherXylem vessels transport water and dissolved mineral ions from the roots to the rest of the plant and also provide structural supportPhloem vessels transport dissolved substances such as sucrose and amino acids from the leaves to the rest of the plant.
The radial conduction of water is the function of the xylem parenchyma. Unlike water sugar is thick and sappy. Diameters and conductivities of xylem and phloem conduits.
The xylem transports water and minerals from the roots up the plant stem and into the leaves. Sieve cells which conduct photosynthates companion cells phloem parenchyma and phloem fibers. Unlike the xylem the phloem tissue is made of columns of living cells swhich contains a cytoplasm but no nucleus and its activities are controlled by a companion cell next to it which has a nucleus but companion.
In different species of plants vascular tissue is arranged differently. Unlike xylem conducting cells. The xylem parenchyma is responsible for storing the prepared food and assists in the conduction of water.
Together phloem and xylem make up a plants vascular system. This is similar to the function of the cambium in dicot roots. Phloem is unlike xylem in that materials can move in both directions in it.
Both phloem and xylem are tubular structures that facilitate easy transportation. Xylem and phloem conduit cell wall. Phloem tissue which transports organic compounds from the site of photosynthesis to other parts of the plant consists of four different cell types.
Plant Tissue System Plant Cell Functions Plant cells are the building blocks of plants. Phloem is unlike xylem in that materials can move in both directions. Xylem is plant tissue that brings water and nutrients up from the roots to the rest of the plant.
In a mature flowering plant or tree most of the cells that make up the xylem are specialised cells. Xylem is the dead permanent tissue that carries water and minerals from roots to all other parts of the plant. Phloem is the complex tissue which acts as a transport system for soluble organic compounds within vascular plants.
While parenchyma cells do occur within what is commonly termed the xylem the more identifiable cells tracheids and vessel elements tend to stain red with Safranin-O. Phloem-It consists of four of elements. Tracheids are the more primitive of the two cell types occurring in the earliest vascular plants.
Water potential evapotranspiration and stomatal regulation influence how water and nutrients are transported in plants. The xylem tissue is located toward the interior of the vascular bundle and phloem is located toward the exterior. Xylem is one of the two types of transport tissue in vascular plants the other being phloemThe basic function of xylem is to transport water from roots to stems and leaves but it also transports nutrients.
It may be either protophloem the cells of which.
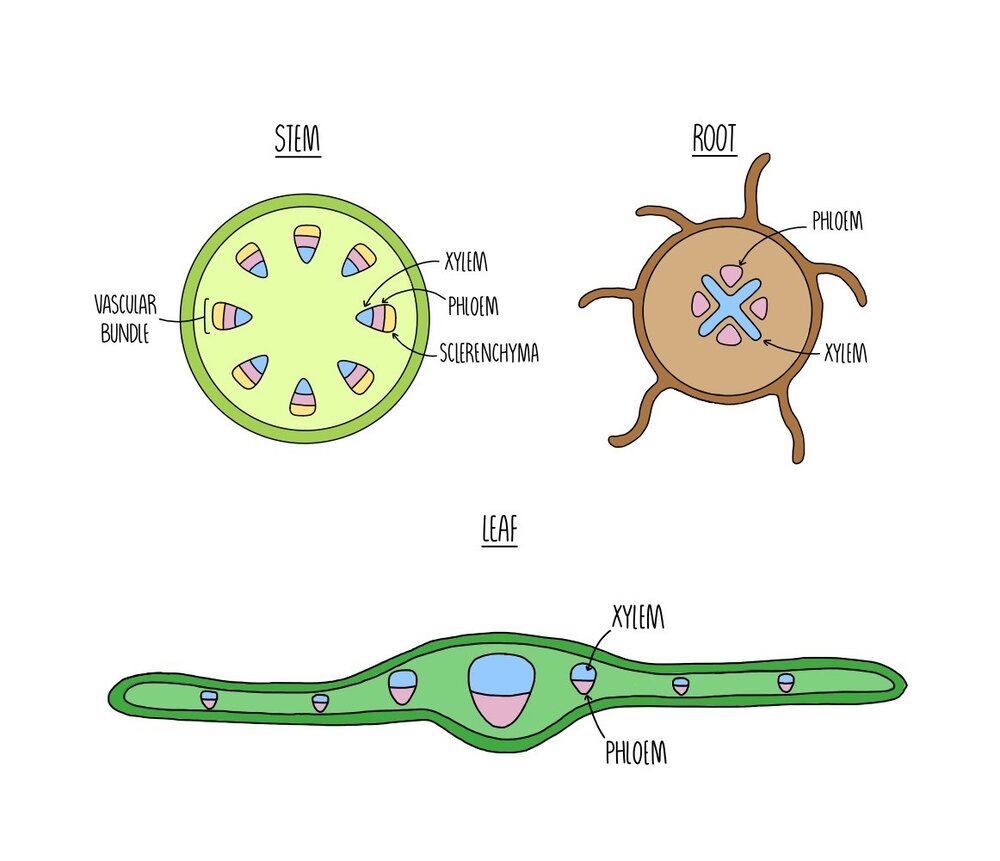
Xylem And Phloem A Level The Science Hive

Vascular Tissue Xylem And Phloem Ppt Video Online Download
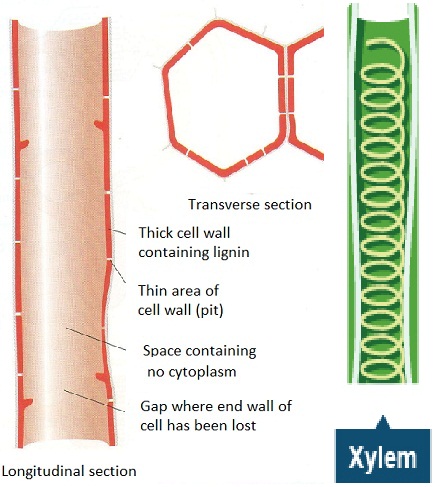
Functions Of Xylem And Phloem Biology Notes For Igcse 2014
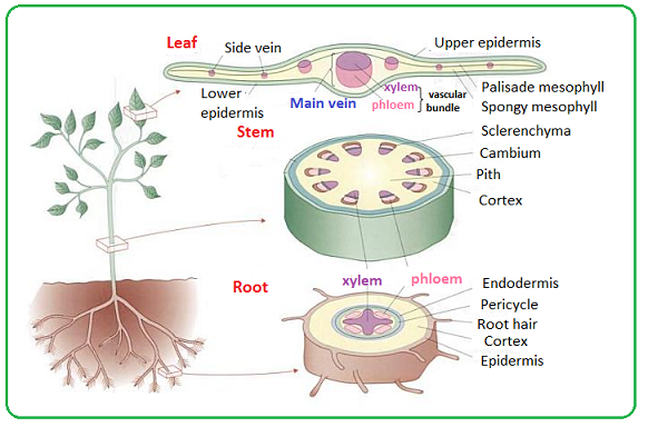
Distribution Of Xylem And Phloem In Roots Stems And Leaves Biology Notes For Igcse 2014
Top 18 Difference Between Xylem And Phloem With Similarities Viva Differences

What Are The Functions Of Xylem And Phloem Brainly In

Xylem And Phloem Structure Exchange And Transport Ep 14 Zoe Huggett Tutorials
Difference Between Xylem And Phloem Pediaa Com
